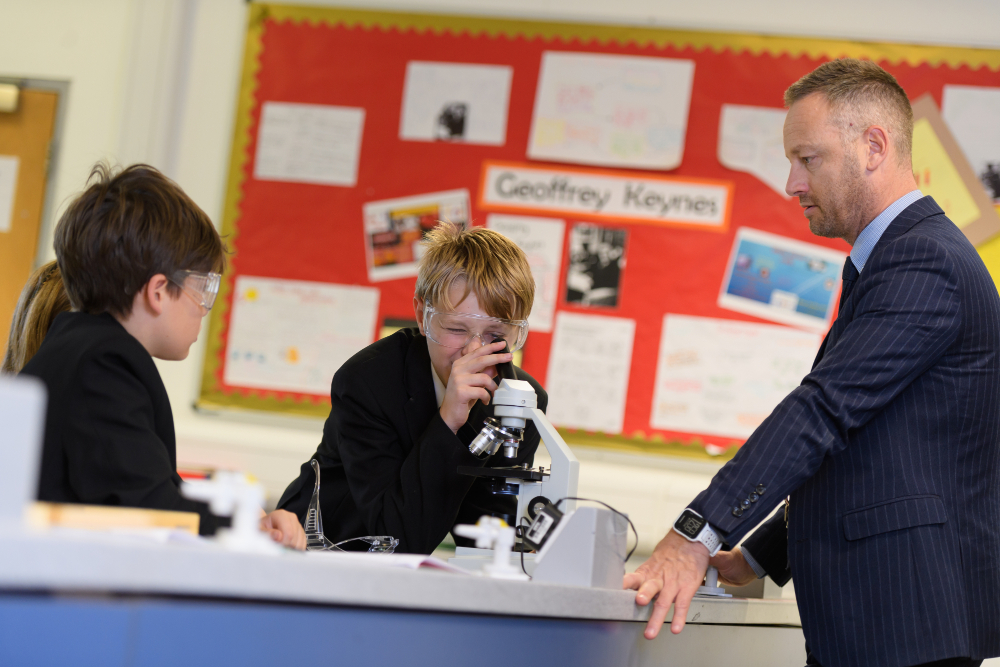
Students in Years 7, 8 and 9 follow the National Curriculum based upon the AQA KS3 scheme of work. Students are encouraged to develop scientific skills to gain an understanding of science through inquisition and discovery. This is further encouraged during March, each year, when students take part in British Science Week themed lessons and activities; with the aim of inspiring and celebrating all the sciences and their importance in our everyday lives. Regular assessment is completed throughout the year using termly assessment which contains a variety of questions to assess different skills. These are used to monitor the progress students make and allow for targeted intervention where appropriate.
Students in Year 10 begin studying the AQA GCSE Combined Science ‘Synergy’ scheme of work. This provides students with a broad approach to science helping them to make links between the different branches of the subject. The progress of students is assessed throughout the year with topic tests and two whole year assessments. Those students who have shown sufficient aptitude for science follow the AQA Separate Sciences curriculum, allowing them to obtain an individual GCSE in Biology, Chemistry and Physics. Students continue to study either Combined Science or Separate Sciences throughout Year 10 and Year 11.

Scientific skills in Years 7 and 8
Scientific attitudes
Experimental skills and investigations
Analysis and evaluation
Measurement
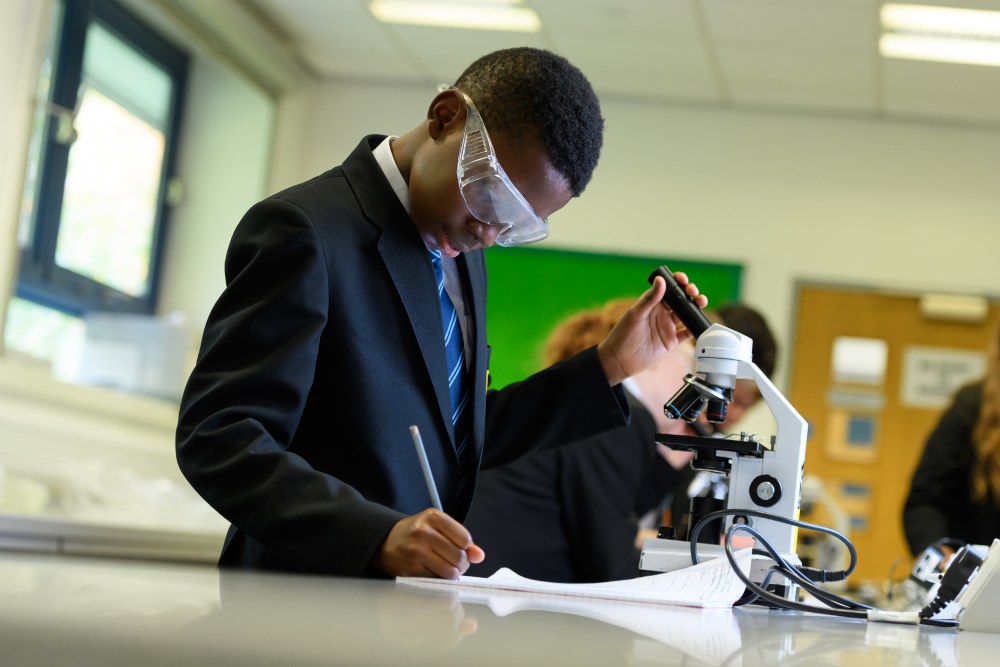
Scientific knowledge and skills in Year 9
The principal focus of science teaching in Year 9 is to develop a deeper understanding of a range of scientific ideas in the subject disciplines of biology, chemistry and physics. Pupils should begin to see the connections between these subject areas and become aware of some of the big ideas underpinning scientific knowledge and understanding. Examples of these big ideas are the links between structure and function in living organisms, the particulate model as the key to understanding the properties and interactions of matter in all its forms, and the resources and means of transfer of energy as key determinants of all of these interactions. Students are also encouraged to relate scientific explanations to phenomena in the world around them and start to use modelling and abstract ideas to develop and evaluate explanations.
Scientific attitudes
Experimental skills and investigations
Analysis and evaluation
Measurement
All of these areas are delivered alongside the department’s homework tool – Tassomai. Students will be introduced to a range of curriculum content from all KS3 areas via Tassomai. This enables them to be ambitious with their learning, pre-learn topics and develop their recall skills.
Autumn
Spring
Summer
Autumn
Spring
Summer
Autumn
Spring
Summer

AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: SYNERGY (8465)
Combined science is divided into two sections. Each section is delivered by a different teacher. Both sections include topics that draw together and apply key concepts. Examples in Life and environmental sciences include Radiation and risk and The Earth’s atmosphere. In these topics, earlier work on atomic structure, waves and electromagnetic radiation is used to explain the effects of different types of radiation on human tissues and on the climate. An example in Physical sciences is Resources of materials and energy, which introduces life cycle assessment as a way of evaluating the impacts of using materials and energy to manufacture useful products.
Required practical
The content in life sciences will be assessed in Paper 1 and 2 of the exams at the end of year 11
Required practical
The content in physical sciences will be assessed in Paper 3 and 4 of the exams at the end of year 11

AQA GCSE PHYSICS (8463)
GCSE specifications in Physics should enable students to:
Content to be examined in paper 1 although some of this content may appear in paper 2.
Content to be examined in paper 2 although some of this content may appear in paper 1.

AQA GCSE BIOLOGY (8461)
The GCSE specification in biology enables students to:
Content to be examined in paper 1 although some of this content may appear in paper 2
Content to be examined in paper 2 although some of this content may appear in paper 1

AQA GCSE CHEMISTRY (8462)
The GCSE specification in chemistry enables students to:
Content to be examined in paper 1 although some of this content may appear in paper 2
Content to be examined in paper 2 although some of this content may appear in paper 1